Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
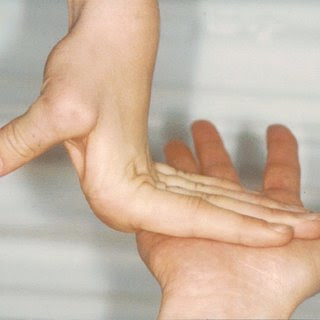 |
Extremely Soft & Velvety Skin is a Sight of Sorrow
|
Medical community is not fully aware of the health issues
that impact women and in most cases, misdiagnose them inappropriately. This is
not an opinion but the result of a study. Similar to many medical conditions
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS) impacts women to a greater extent which even
accounts for the delay in proper diagnosis and treatment.
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS)
One of my friends was always accident-prone. She skid and
fell on the road every other time as though she was let down by a banana peel,
handled dishes clumsily letting them fall over many-a-time and was always
reprimanded by parents, friends and colleagues for this unskilled behavior. She
could not even pick a wooden chair and move it to another place. A few year
back, when she tried to help me move a couch up a three-storied apartment, she
could not get out of bed for an entire week! Off late, she had been complaining
of constant bone-deep aching pain as though her hips had been pricked by broken
glass all over. Even physical therapists could not understand the reason for
such incessant and intense pain without any participation in sports activities
or neck-breaking injuries. When this friend of mine chanced to meet a
geneticist some time back, the physician diagnosed her with Type III of a rare
connective tissue disorder known as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS).
EDS are a group of rare connective tissue disorders that can
be inherited and varied in both, affecting the body. They are mostly
characterized by joint hypermobility (joints that stretch beyond normalcy),
skin hyperextensibility (skins that stretch beyond normalcy) and tissue
fragility. Connective tissues are the ones that provide support to skin,
ligaments, tendons, blood vessels, internal organs and bones. Rare diseases
rarely have treatments options and people with these diseases bear its pain
throughout life. For more details on rare diseases, please visit the website www.firsteatright.com.
EDS Types & Gene Influence
As of 2017, there are 13 types of EDS and each of these
types are caused by faults in certain genes that weaken the connective tissue.
Based on the type of EDS, the gene might have been acquired from one parent or
both. Rarely, the gene is not acquired but occurs for the first time in the
person. EDS affects different people in different ways. The diseases might be
mild in some people, can disable some others and rarely, can be
life-threatening to a handful few. If you have one of the common forms of EDS, there’s
a 50% chance that you’ll pass on the gene to your offspring.
Hypermobile EDS is the main type while rarer ones include
classical EDS, vascular EDS and kyphoscoliosis EDS.
Hypermobile EDS (hEDS)
This is often very similar to another condition called as
joint hypermobility syndrome. People with hEDS may experience extreme
tiredness, easily bruising skin, joint hypermobility, joint pain and clicking
joints, bladder control problems, loose joints that dislocate easily and
digestive problems. There is no specific test to confirm hEDS and it is
confirmed based on a person’s medical history and physical examination.
Classical EDS
This affects the skin more often and is less common than
hEDS. Joint hypermobility, stretchy skin, loose joints that dislocate easily,
smooth, velvety skin that bruise easily, slow-healing wounds that leave a wide
scar and fragile skin are commonly experienced by people with classical EDS.
Vascular EDS (vEDS)
This is a rare type but often considered as the most serious
type of EDS as it affects the internal organs and blood vessels which can break
them open and result in life-threatening bleeding. Individuals with vEDS may
have skin that bruises easily, very thin skin with visible blood vessels,
especially on the upper chest and legs, organ problems such as bowel or womb
tearing, unusual facial features such as thin nose and lips, large eyes and
small earlobes and delayed wound healing.
Kyphoscoliotic EDS (kEDS)
This condition is rare and is manifested by joint
hypermobility, loose, unstable joints that dislocate easily, weak muscle tone
from childhood (hypotonia) that can cause delay in sitting and walking and the
person might also face walking difficulty if the symptoms get worse, fragile
eyes that can be easily damaged and soft, velvety skin that can bruise easily.
Treatment
There is no medication and cure available for EDS. Treatment
can help you cope with pain and improve quality of life.
Medications: Physician might prescribe pain killers
to relieve pain and heal acute injuries. The doctor might also recommend that
you maintain a low blood pressure. That’s because blood vessels are too fragile
in some types of EDS and the stress on these vessels is reduced when BP is
maintained at a lower level.
Physical therapy: Joints with fragile connective
tissues are likelier to dislocate. Exercises to strengthen the muscles and
stabilize joints are the primary treatment procedures although your physician
might suggest specific braces to help prevent joint dislocations.
Surgery: This is recommended to repair joint damage
due to repeated dislocations. Skin and connective tissues mostly don’t heal
completely after the surgery.
Lifestyle: Interested in sports? Choose swimming,
walking, tai chi, recreational biking, elliptical machine or a stationary bike
that minimizes stress on your hips, knees and ankles. Stay away from
weightlifting. Protect your jaw joint by avoiding chewing gum, hard rolls and
ice that can break your jaws.


Comments
Post a Comment